According to Wikipedia, a chain reaction is a sequence of reactions where a reactive product or by-product causes additional reactions to take place. In a chain reaction, positive feedback leads to a self-amplifying chain of events. A nuclear chain reaction was proposed by Leo Szilard in 1933, after the neutron was discovered, more than five years before nuclear fission was first discovered. The self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction is the principle for nuclear reactors and atomic bombs.
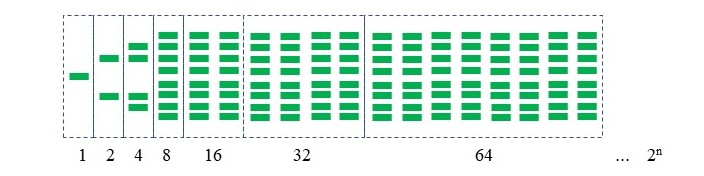
We are here talking about a biochemical chain reaction that has nothing to do with a nuclear chain reaction. This chain reaction is called Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), an enzymatic biochemical reaction, was discovered by Kary Mullis in 1983. During PCR, a specific region of a DNA strand is amplified under defined thermal cycling conditions. The number of DNA molecules is increased exponentially as the cycle number increases (see the above diagram). As a result, PCR can be used to detect a small amount of initial DNA molecules from a biological organism such as microorganisms, plant, animal, and humans. The PCR technology has been widely used for gene detection such as cancer screening and disease screening for both animal health and human health. This also applies to gene detection in plants for breeding and genotyping. Some PCR tests have been developed to detect pathogens that cannot be detected with traditional culture methods. However, challenges still exist for the development of PCR tests for the detection of living and viable pathogens. At Cicadea Biotech, we can develop PCR-based tests or assays for gene detection and microbial detection.
